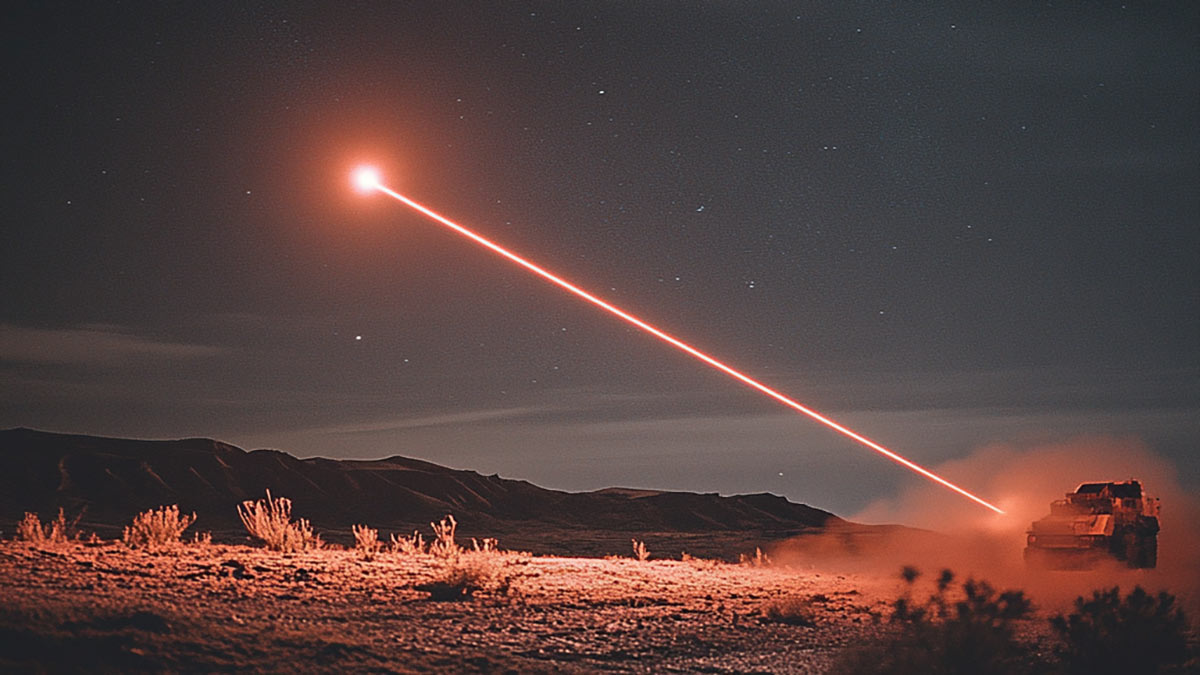
Fraunhofer EMI is developing powerful software that simulates complex laser-matter interactions and evaluates the effects of laser weapons.
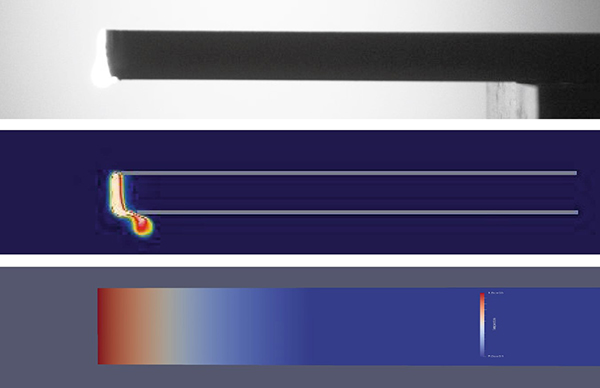
Fraunhofer EMI is developing innovative software that simulates complex laser-matter interactions for defense applications and evaluates the effects of laser weapons. It also offers potential for other areas of application. The researchers use state-of-the-art mathematical methods to master the challenges. When objects are irradiated with high-energy lasers with a power of over 100 kW and beam radii in the millimeter to centimeter range, numerous physical effects occur. These include heat conduction in solids, fluid dynamic effects after phase transitions and chemical reactions such as oxidation processes that are caused by the thermal effect of the laser. The complexity of these coupled processes overwhelms currently available software solutions, so that adequate and high-performance simulation is only possible to a limited extent. To overcome these challenges, Fraunhofer EMI is developing problem-oriented, modular modeling approaches. These weight the model equations based on the dominant sub-processes, while ignoring less relevant effects. To implement this idea, a software environment was developed that enables the implementation of physical-mathematical models as partial differential equations on dynamic computing domains. The numerical infrastructure is based on the discontinuous Galerkin method, which combines concepts of finite volume and finite element methods. This method enables efficient simulations through adaptive resolution adjustment and is characterized by high parallelizability. The newly developed software has an impressive modular structure and already fulfills other defence technology purposes. In addition to laser-matter interaction, it simulates the propagation of thermal radiation through the near-Earth atmosphere, for example.
